×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Subaru Parts
- Subaru Accessories


My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Subaru Impreza Fuse
Circuit Fuse- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
45 Fuses found
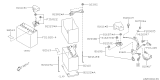
Subaru Impreza FUSIBLE Link SBF 80A
Part Number: 82211AG150$35.14 MSRP: $50.93You Save: $15.79 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days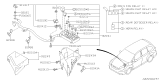
Subaru Impreza Fuse-Auto
Part Number: 82210FC010$1.25 MSRP: $1.77You Save: $0.52 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Subaru Impreza Mini Fuse 10A
Part Number: 82210AJ10A$1.09 MSRP: $1.84You Save: $0.75 (41%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Subaru Impreza Mini Fuse 20A
Part Number: 82210AJ20A$1.09 MSRP: $1.84You Save: $0.75 (41%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Subaru Impreza Fuse-Main
Part Number: 82211FC080$4.06 MSRP: $5.73You Save: $1.67 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Subaru Impreza Mini Fuse 10A
Part Number: 82210AJ100$1.09 MSRP: $1.84You Save: $0.75 (41%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Subaru Impreza Slow Blower Fuse 80A
Part Number: 82211AJ81A$7.81 MSRP: $11.03You Save: $3.22 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Subaru Impreza Fuse-Main
Part Number: 82211FC030$2.37 MSRP: $3.35You Save: $0.98 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Subaru Impreza Fuse-Main
Part Number: 82211FC050$2.66 MSRP: $3.75You Save: $1.09 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Subaru Impreza Fuse-Auto
Part Number: 82210FC015$1.03 MSRP: $1.74You Save: $0.71 (41%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Subaru Impreza Fuse Auto
Part Number: 82210FC030$1.25 MSRP: $1.77You Save: $0.52 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Subaru Impreza Fuse-Auto
Part Number: 82210FC020$1.03 MSRP: $1.74You Save: $0.71 (41%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Subaru Impreza Mini Fuse 15A
Part Number: 82210AJ15A$1.09 MSRP: $1.84You Save: $0.75 (41%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Subaru Impreza Slow Blower Fuse 40A
Part Number: 82211AJ40A$2.67 MSRP: $3.77You Save: $1.10 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysSubaru Impreza Slow Blower Fuse
Part Number: 82211AL12A$6.49 MSRP: $9.17You Save: $2.68 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysSubaru Impreza Mini Fuse 25A
Part Number: 82210FC025$0.58 MSRP: $0.98You Save: $0.40 (41%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysSubaru Impreza Slow Blower Fuse A380A
Part Number: 82211AJ810$9.48 MSRP: $13.38You Save: $3.90 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
| Page 1 of 3 |Next >
1-20 of 45 Results
Subaru Impreza Fuse
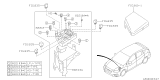
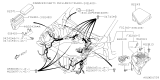
The Fuse in Subaru Impreza vehicles functions as an essential safety element that protects electrical components through a current interruption in overcurrent events. The metal wire functions as the Fuse mechanism because it melts itself when it encounters too much current thereby shutting off electrical currents. A Fuse box resides beneath the hood to protect radio and light components from damage that might result from whole body vibration along with moisture exposure. Relays inside this box steer electrical power to these components. Subaru Impreza vehicles employ blade Fuses among their Fuse types since these components exhibit different sizes and color codes representing individual amperage specifications. Drug tube Fuses were utilized in past models of vehicles up to 1981. Modern vehicles primarily use blade replacement units as their primary protective element but differ in their basic construction and usage principles. Keeping Subaru Impreza replacement parts properly maintained and replacing them in time remains vital for enabling all vehicle part to operate correctly.
Our website stands as the go-to online destination for OEM Subaru Impreza Fuse. With complete lines of genuine Subaru Impreza Fuse available at unbeatable market prices, we ensure top quality, reliability, and durability. Each part comes backed by the manufacturer's warranty, reinforcing your trust in our offerings.
Subaru Impreza Fuse Parts Questions & Experts Answers
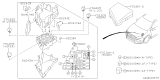
- Q: How to check and replace fuses, fusible links, and circuit breakers on Subaru Impreza?A:A combination of fuses, circuit breakers and fusible links protects the vehicle's electrical circuits. There are two fuse boxes: one in the engine compartment and the other in the passenger compartment. The engine compartment fuse box is positioned at the left side of the engine compartment whereas the passenger compartment fuse box is located at the left end of the instrument panel. Every fuse has a specific purpose and included inside the fuse box cover is a spare fuses as well as removal tool. These use miniaturized blade terminal design for easy replacement or removal from a circuit. Using a test light, power can be checked at exposed terminal tips to ascertain if it's present on one side but missing on another side meaning that it's blown out completely. By simply plugging out an old fuse and inserting with new of same type together with amperage rating will be best way to go when replacing blown ones because they do not require any additional technical steps apart from just exactly doing what their names imply. Fusible links are employed where there may not be any need for ordinary fusing, or where high currents flow through them; therefore, these kinds of linkages can be substituted by obtaining another piece having similar amps. Circuit breakers usually protect certain circuits and are mostly located under an instrument panel. They reset automatically; however, if a circuit does not turn back on again after resetting it should be checked immediately. When checking a circuit breaker one must pull it slightly up so as to probe with voltmeter while each end should have battery voltage whereby only having voltage at one end means that such circuit breaker ought to be changed therefore providing evidence supporting this test result. Manual resetting applies in some cases to certain types of these devices.
Related Subaru Impreza Parts
Browse by Year
2025 Fuse 2024 Fuse 2023 Fuse 2022 Fuse 2021 Fuse 2020 Fuse 2019 Fuse 2018 Fuse 2017 Fuse 2016 Fuse 2015 Fuse 2014 Fuse 2013 Fuse 2012 Fuse 2011 Fuse 2010 Fuse 2009 Fuse 2008 Fuse 2007 Fuse 2006 Fuse 2005 Fuse 2004 Fuse 2003 Fuse 2002 Fuse 2001 Fuse 2000 Fuse 1999 Fuse 1998 Fuse 1997 Fuse 1996 Fuse 1995 Fuse 1994 Fuse 1993 Fuse